Tetrahedral Metrics
automesh metrics tet --help
Quality metrics for an all-tetrahedral finite element mesh
Usage: automesh metrics tet [OPTIONS] --input <FILE> --output <FILE>
Options:
-i, --input <FILE> Mesh input file (exo | inp | stl)
-o, --output <FILE> Quality metrics output file (csv | npy)
-q, --quiet Pass to quiet the terminal output
-h, --help Print help
automesh implements the following tetrahedral element quality metrics1:
- Maximum edge ratio
- Minimum scaled Jacobian
- Maximum skew
- Element volume
A brief description of each metric follows.
Maximum Edge Ratio
- measures the ratio of the longest edge to the shortest edge in a mesh element.
- A ratio of 1.0 indicates perfect element quality, whereas a very large ratio indicates bad element quality.
- Knupp et al.1 (page 63) indicate an acceptable range of
[1.0, 3.0].
Minimum Scaled Jacobian
- evaluates the determinant of the Jacobian matrix at each of the corners nodes (and the Jacobian itself1 page 71), normalized by the corresponding edge lengths, and returns the minimum value of those evaluations.
- Knupp et al.1 (page 75) indicate an acceptable range of
[0.5, sqrt(2)/2][0.5, 0.707]. - A scaled Jacobian close to
0indicates that the tetrahedra is poorly shaped (e.g., very thin or degenerate), which can lead to numerical instability. - A scaled Jacobian of
1indicates that the tetrahedra is equilateral, which is the ideal shape for numerical methods.
Maximum Skew
- Skew measures how much an element deviates from being a regular shape (e.g., in 3D a cube or a regular tetrahedron; in 2D a square or equilateral triangle). A skew value of 0 indicates a perfectly regular shape, while higher values indicate increasing levels of distortion.
- Knupp et al.1 does not give a definition of skew for tetrahedra, so we provide our definition below. For any triangle composing the four faces of a tetrahedron, where is the smallest angle of the triangle,
- The maximum skew of a tetrahedron is the maximum skew of all of the four triangular faces (see Triangular Metrics, Maximum Skew).
- For an equilateral (regular) tetrahedron, and .
- In the limit as .
Element Volume
- Measures the volume of the element (see Knupp et al.1, page 61).
Unit Tests
We verify the following element qualities:
| tetrahedron | volume | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
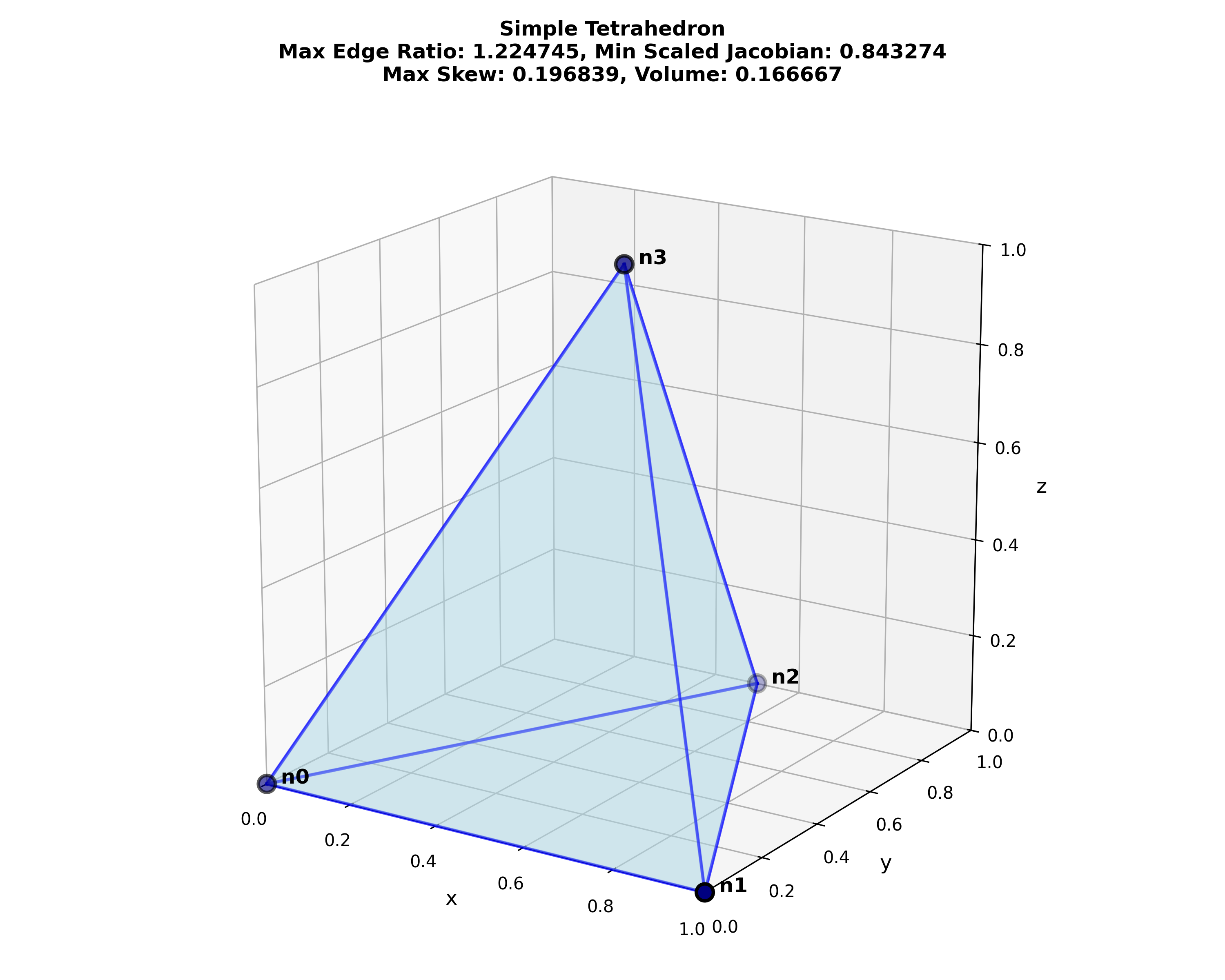
| simple | 1.225 | 0.843 [0.843] | 0.197 | 0.167 [0.167] |
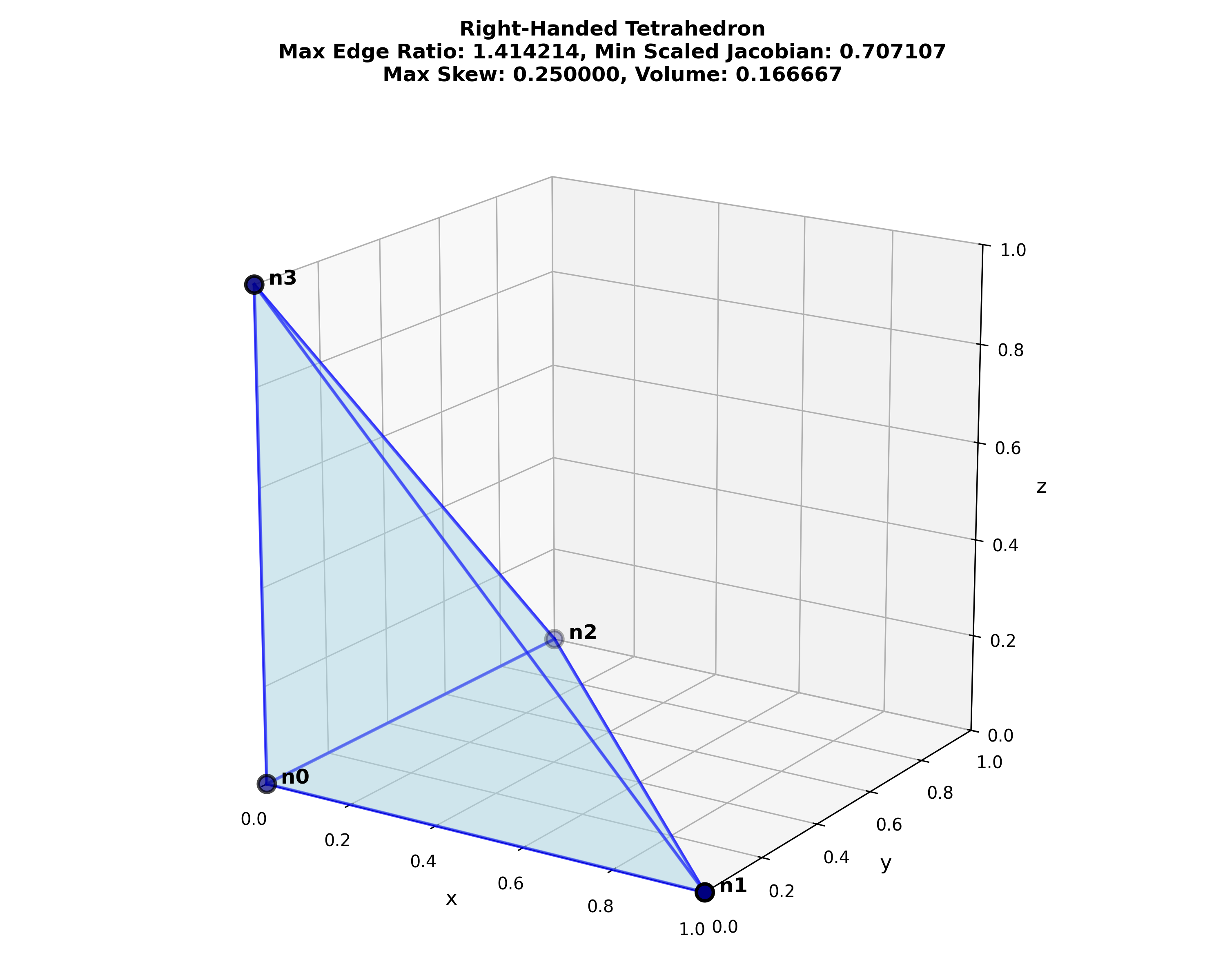
| right-handed | 1.414 | 0.707 [0.707] | 0.250 | 0.167 [0.167] |
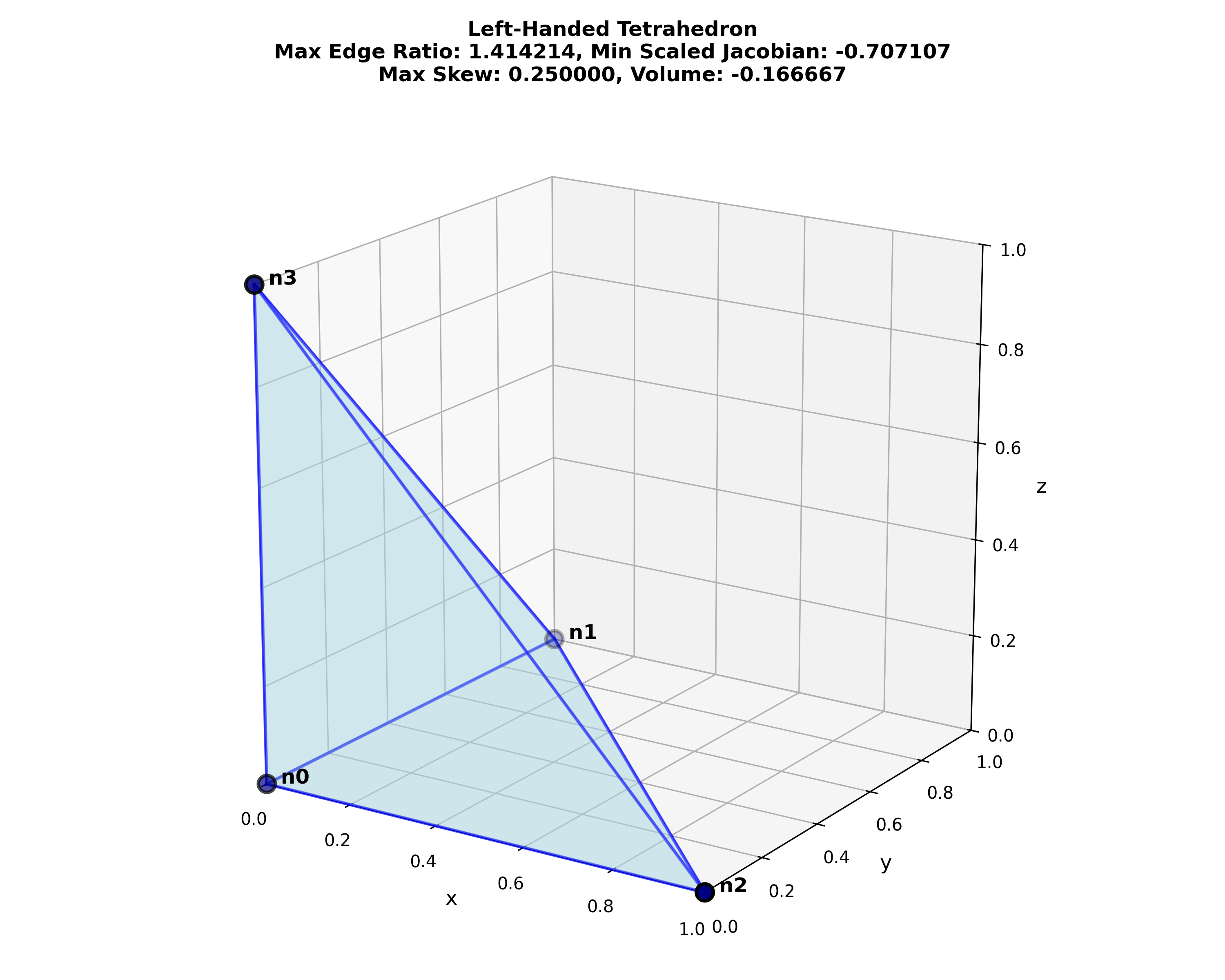
| left-handed | 1.414 | -0.707 [-0.707] | 0.250 | -0.167 [-0.167] |
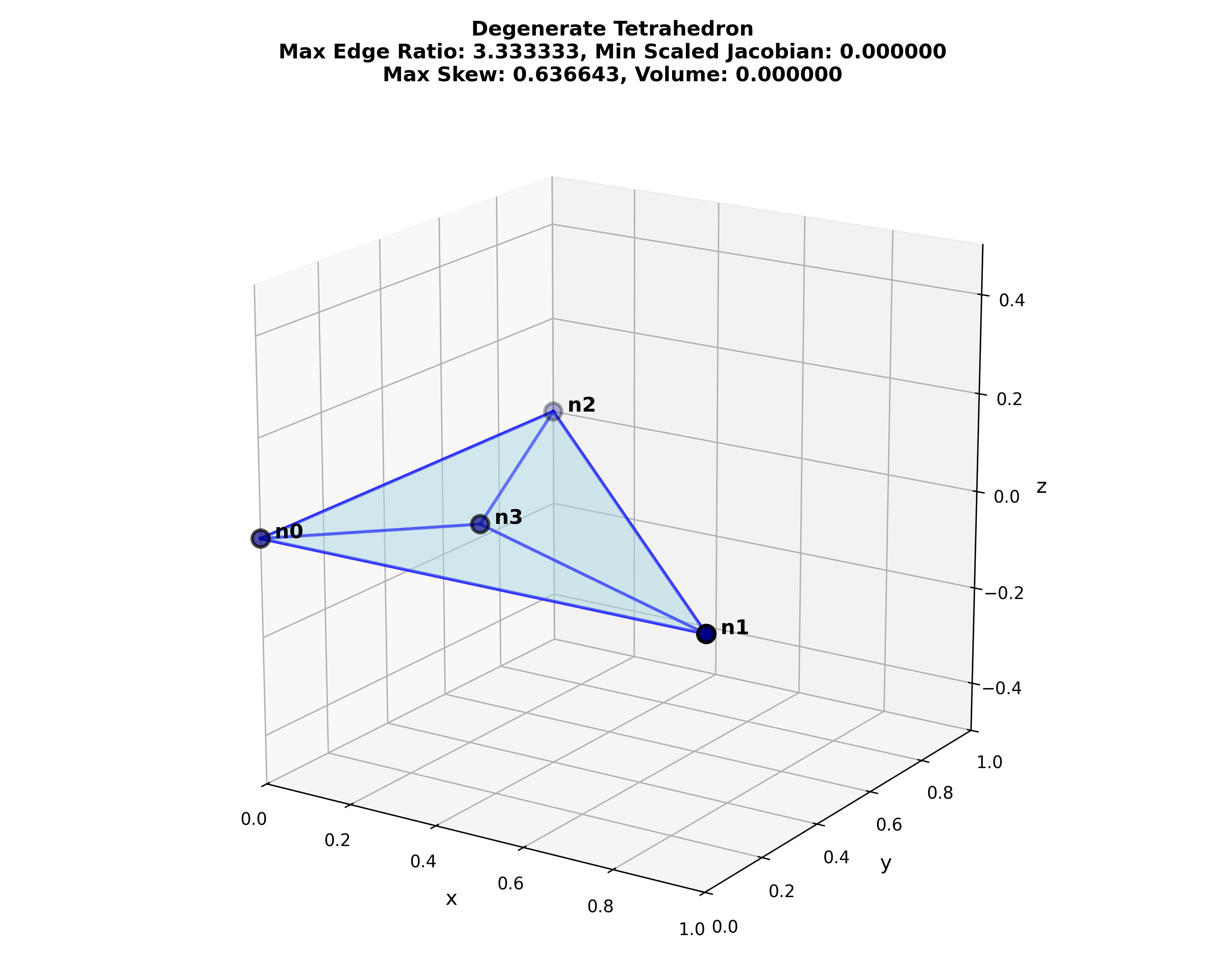
| degenerate | 3.33 | 0.000 [0.000] | 0.637 | 0.000 [0.000] |
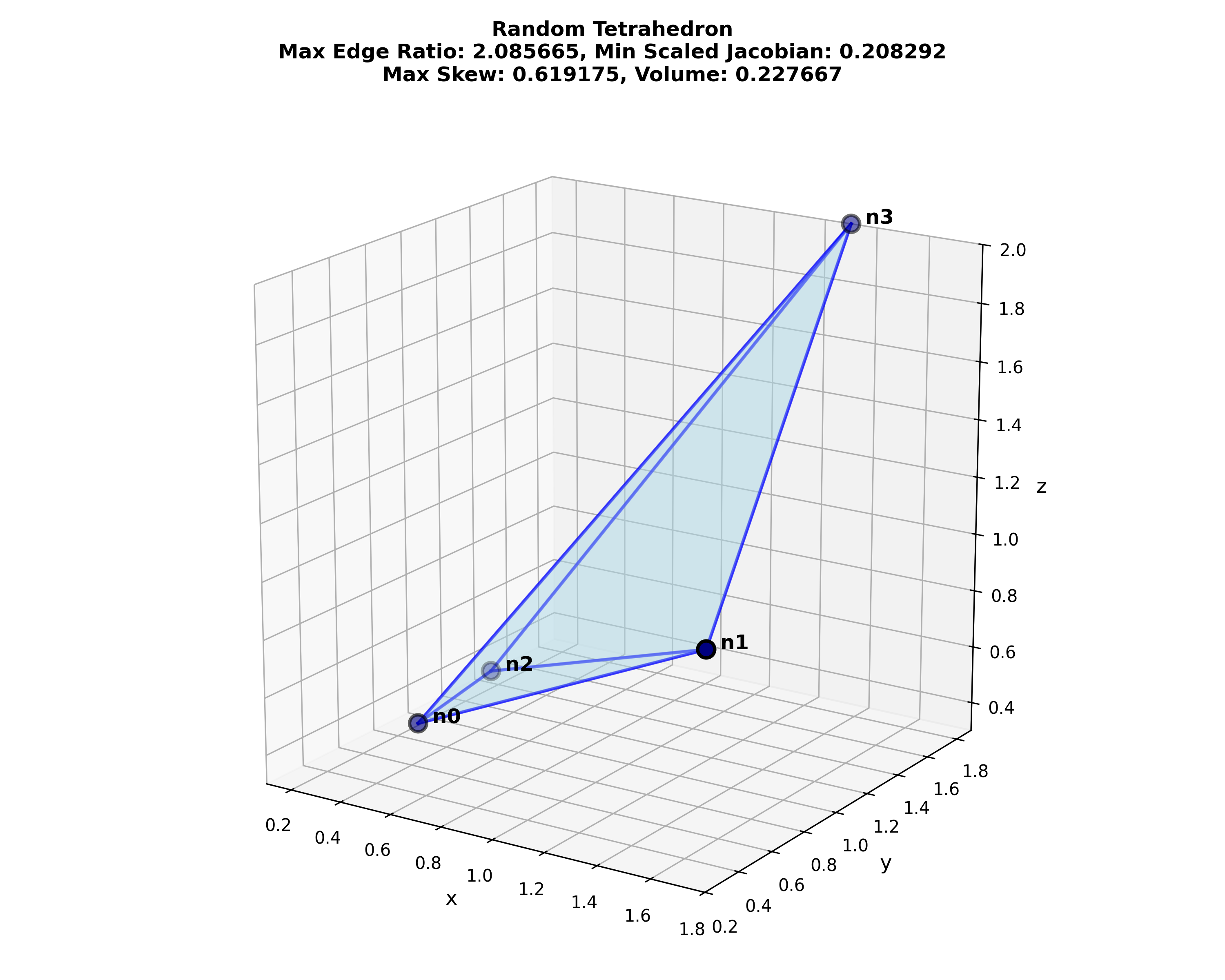
| random | 2.086 | 0.208 [0.208] | 0.619 | 0.228 [0.228] |
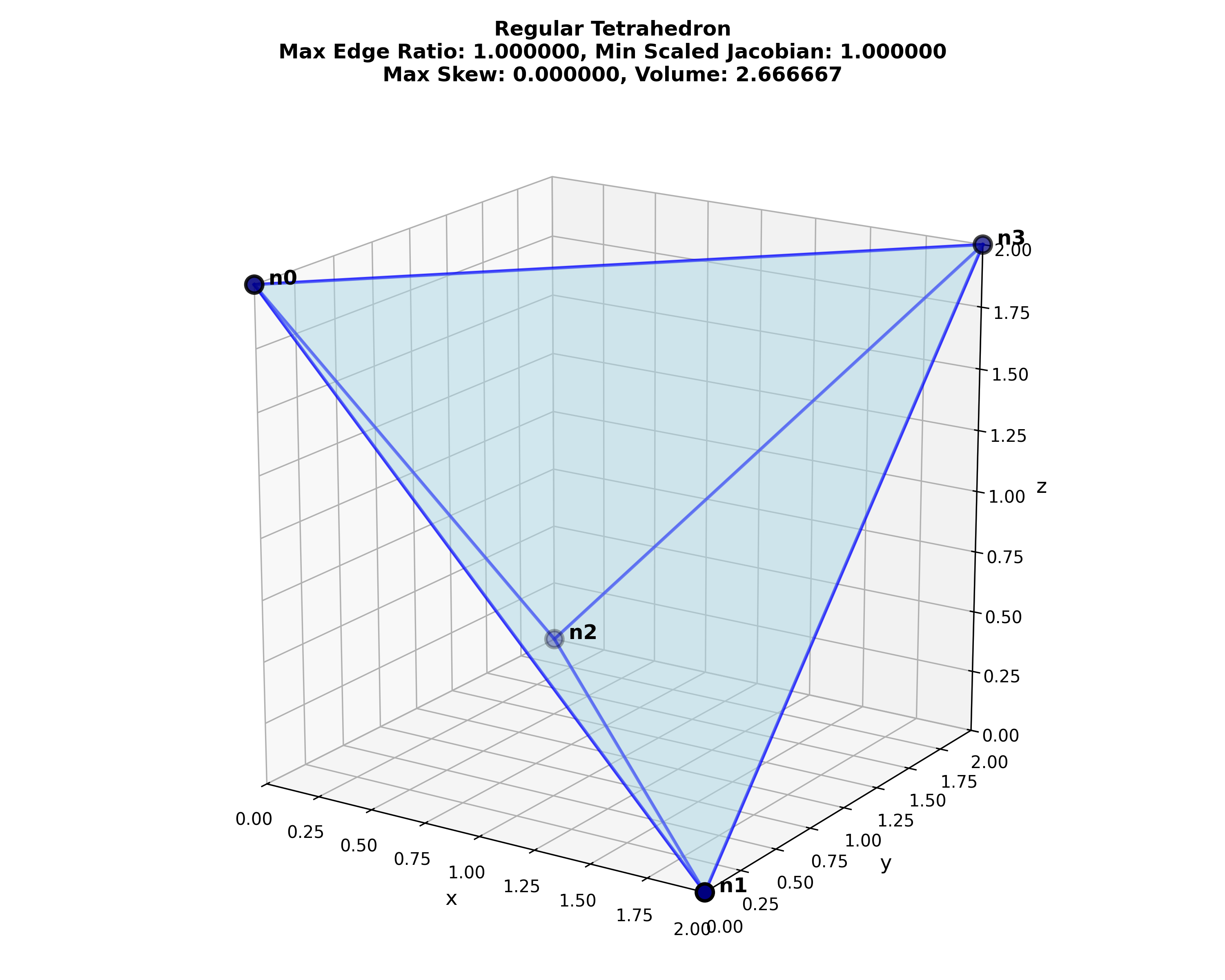
| regular | 1.000 | 1.000 [1.000] | 0.000 | 2.667 [2.667] |
Figure: Tetrahedral metrics. Leading values are from automesh. All values agree with an independent Python calculation, (see metrics_tetrahedral.py) in double precision with a tolerance of less than 1.00e-14. Values in [brackets], minimum scaled Jacobian and volume, also agree with Cubit. Cubit does not compute edge ratio and skew for tetrahedral elements. Cubit uses the term Aspect Ratio; it is not the same as Edge Ratio.
Figure: Python visualization of the tetrahedron test cases, created with metrics_tetrahedral.py.
Local Numbering Scheme
Nodes
The local numbering scheme for nodes of a tetrahedral element:
3
/|\
L3 / | \ L5
/ | \
0---|---2 (horizontal line is L2)
\ | /
L0 \ | / L1
\|/
1
(vertical line is L4)
where
L0 = p1 - p0 L3 = p3 - p0
L1 = p2 - p1 L4 = p3 - p1
L3 = p0 - p2 L5 = p3 - p2
| node | connected nodes |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| 1 | 0, 2, 3 |
| 2 | 0, 1, 3 |
| 3 | 0, 1, 2 |
Faces
A tetrahedron has four triangular faces. The faces are typically numbered opposite to the node they do not contain (e.g., face 0 is opposite to node 0).
From the exterior of the element, view the (0, 1, 3) face and upwarp the remaining faces; the four face normals now point out out of the page. The local numbering scheme for faces of a tetrahedral element:
2-------3-------2
\ 1 / \ 0 /
\ / \ /
\ / 2 \ /
0-------1
\ 3 /
\ /
\ /
2
| face | nodes |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| 1 | 0, 2, 3 |
| 2 | 0, 1, 3 |
| 3 | 0, 1, 2 |
Source
metrics_tetrahedral.py
"""Visualize various tetrahedra and calculate quality metrics."""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection
from typing import List, Tuple
def calculate_edge_vectors(nodes: np.ndarray) -> List[np.ndarray]:
"""Calculate the six edge vectors of a tetrahedron.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
Returns:
List[np.ndarray]: A list containing six 1D numpy arrays, each
representing an edge vector.
"""
# Base edges (in a cycle 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0)
e0 = nodes[1] - nodes[0] # n1 - n0
e1 = nodes[2] - nodes[1] # n2 - n1
e2 = nodes[0] - nodes[2] # n0 - n2
# Edges connecting the apex (node 3)
e3 = nodes[3] - nodes[0] # n3 - n0
e4 = nodes[3] - nodes[1] # n3 - n1
e5 = nodes[3] - nodes[2] # n3 - n2
return [e0, e1, e2, e3, e4, e5]
def signed_element_volume(nodes: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""Calculate the signed volume of a tetrahedron.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
Returns:
float: The signed volume of the tetrahedron.
"""
v0, v1, v2, v3 = nodes
return np.dot(np.cross(v1 - v0, v2 - v0), v3 - v0) / 6.0
def maximum_edge_ratio(nodes: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""Calculate the maximum edge ratio (max_length / min_length) of a tetrahedron.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
Returns:
float: The maximum edge ratio. Returns `float('inf')` if the minimum
edge length is zero.
"""
edge_vectors = calculate_edge_vectors(nodes)
lengths = [np.linalg.norm(v) for v in edge_vectors]
min_length = min(lengths)
max_length = max(lengths)
if min_length == 0:
return float("inf")
return float(max_length / min_length)
def minimum_scaled_jacobian(nodes: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""Calculate the minimum scaled Jacobian quality metric for a tetrahedron.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
Returns:
float: The minimum scaled Jacobian value. Returns 0.0 if the maximum
nodal Jacobian is zero.
"""
# The element Jacobian j is 6.0 times the signed element volume
j = signed_element_volume(nodes) * 6.0
# Get all six edge lengths
edge_vectors = calculate_edge_vectors(nodes)
els = [np.linalg.norm(v) for v in edge_vectors]
# Compute the four nodal Jacobians
lambda_0 = els[0] * els[2] * els[3]
lambda_1 = els[0] * els[1] * els[4]
lambda_2 = els[1] * els[2] * els[5]
lambda_3 = els[3] * els[4] * els[5]
# Find the maximum of the nodal Jacobians (including the element Jacobian)
lambda_max = max([j, lambda_0, lambda_1, lambda_2, lambda_3])
# Calculate the final quality metric
if lambda_max == 0.0:
return 0.0 # Avoid division by zero for collapsed elements
else:
return j * np.sqrt(2.0) / lambda_max
def face_minimum_angle(
nodes: np.ndarray, n0_idx: int, n1_idx: int, n2_idx: int
) -> float:
"""Calculate the minimum angle of a triangular face.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
n0_idx (int): Index of the first node of the face.
n1_idx (int): Index of the second node of the face.
n2_idx (int): Index of the third node of the face.
Returns:
float: The minimum angle (in radians) of the triangular face.
"""
v0 = nodes[n0_idx]
v1 = nodes[n1_idx]
v2 = nodes[n2_idx]
l0 = v2 - v1
l1 = v0 - v2
l2 = v1 - v0
# Normalize
l0 = l0 / np.linalg.norm(l0)
l1 = l1 / np.linalg.norm(l1)
l2 = l2 / np.linalg.norm(l2)
flip = -1.0
angles = [
np.arccos(np.clip(np.dot(l0 * flip, l1), -1.0, 1.0)),
np.arccos(np.clip(np.dot(l1 * flip, l2), -1.0, 1.0)),
np.arccos(np.clip(np.dot(l2 * flip, l0), -1.0, 1.0)),
]
return min(angles)
def face_maximum_skew(
nodes: np.ndarray, n0_idx: int, n1_idx: int, n2_idx: int
) -> float:
"""Calculate the maximum skew for a single triangular face of a tetrahedron.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
n0_idx (int): Index of the first node of the face.
n1_idx (int): Index of the second node of the face.
n2_idx (int): Index of the third node of the face.
Returns:
float: The maximum skew value for the triangular face.
"""
tolerance = 1e-9
equilateral_rad = np.pi / 3.0 # 60 degrees in radians
minimum_angle = face_minimum_angle(nodes, n0_idx, n1_idx, n2_idx)
if abs(equilateral_rad - minimum_angle) < tolerance:
return 0.0
else:
return (equilateral_rad - minimum_angle) / equilateral_rad
def maximum_skew(nodes: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""Calculate the maximum skew across all four faces of the tetrahedron.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
Returns:
float: The maximum skew value among all faces of the tetrahedron.
"""
# A tetrahedron has four faces, so calculate the skew for each and
# then take the maximum
skews = [
face_maximum_skew(nodes, 0, 1, 2),
face_maximum_skew(nodes, 0, 1, 3),
face_maximum_skew(nodes, 0, 2, 3),
face_maximum_skew(nodes, 1, 2, 3),
]
return max(skews)
def visualize_tetrahedron(
nodes: np.ndarray,
title: str = "Tetrahedron",
show_edges: bool = True,
show_labels: bool = True,
save_figure: bool = False,
) -> Tuple[plt.Figure, plt.Axes]:
"""Visualize a tetrahedron given its four node coordinates and display quality metrics.
Args:
nodes (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array of shape (4, 3)
representing the coordinates of the four nodes
of the tetrahedron.
title (str, optional): Title for the plot. Defaults to "Tetrahedron".
show_edges (bool, optional): Whether to display the edges of the tetrahedron.
Defaults to True.
show_labels (bool, optional): Whether to display labels for the nodes.
Defaults to True.
save_figure (bool, optional): Whether to save the figure as a PNG file.
Defaults to False.
Returns:
Tuple[plt.Figure, plt.Axes]: A tuple containing the matplotlib Figure and Axes objects.
"""
nodes = np.array(nodes)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection="3d")
# Define the four faces of the tetrahedron
# Each face is a triangle defined by three nodes
faces = [
[nodes[0], nodes[1], nodes[2]], # Face 0-1-2
[nodes[0], nodes[1], nodes[3]], # Face 0-1-3
[nodes[0], nodes[2], nodes[3]], # Face 0-2-3
[nodes[1], nodes[2], nodes[3]], # Face 1-2-3
]
# Create the 3D polygon collection for faces
face_collection = Poly3DCollection(
faces, alpha=0.3, facecolor="lightblue", edgecolor="blue", linewidths=1.5
)
ax.add_collection3d(face_collection)
# Plot nodes
ax.scatter(
nodes[:, 0],
nodes[:, 1],
nodes[:, 2],
c="navy",
s=100,
marker="o",
edgecolors="black",
linewidths=2,
)
# Add node labels
if show_labels:
for i, node in enumerate(nodes):
ax.text(
node[0], node[1], node[2], f" n{i}", fontsize=12, fontweight="bold"
)
# Draw edges if requested
if show_edges:
edges = [
(0, 1),
(1, 2),
(2, 0), # Base triangle
(0, 3),
(1, 3),
(2, 3), # Edges to apex
]
for edge in edges:
points = nodes[list(edge)]
ax.plot3D(*points.T, "b-", linewidth=2, alpha=0.6)
# Calculate all metrics
volume = signed_element_volume(nodes)
max_edge_ratio = maximum_edge_ratio(nodes)
min_scaled_jac = minimum_scaled_jacobian(nodes)
max_skew = maximum_skew(nodes)
# Set labels and title
ax.set_xlabel("x", fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel("y", fontsize=12)
ax.set_zlabel("z", fontsize=12)
title_text = f"{title}\n"
title_text += f"Max Edge Ratio: {max_edge_ratio:.6f}, "
title_text += f"Min Scaled Jacobian: {min_scaled_jac:.6f}\n"
title_text += f"Max Skew: {max_skew:.6f}, "
title_text += f"Volume: {volume:.6f}"
ax.set_title(title_text, fontsize=12, fontweight="bold")
# Set equal aspect ratio
max_range = (
np.array(
[
nodes[:, 0].max() - nodes[:, 0].min(),
nodes[:, 1].max() - nodes[:, 1].min(),
nodes[:, 2].max() - nodes[:, 2].min(),
]
).max()
/ 2.0
)
mid_x = (nodes[:, 0].max() + nodes[:, 0].min()) * 0.5
mid_y = (nodes[:, 1].max() + nodes[:, 1].min()) * 0.5
mid_z = (nodes[:, 2].max() + nodes[:, 2].min()) * 0.5
ax.set_xlim(mid_x - max_range, mid_x + max_range)
ax.set_ylim(mid_y - max_range, mid_y + max_range)
ax.set_zlim(mid_z - max_range, mid_z + max_range)
# ax.view_init(elev=63, azim=-110, roll=0)
ax.view_init(elev=18, azim=-57, roll=0)
ax.set_aspect("equal")
plt.tight_layout()
if save_figure:
filename = title.replace(" ", "_").lower() + ".png"
plt.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
print(f"Saved figure to {filename}")
return fig, ax
# Example 1: Simple tetrahedron
NAME = "Simple Tetrahedron"
print(f"Example 1: {NAME}")
nodes_1 = np.array(
[
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.5, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.5, 0.5, 1.0],
]
)
visualize_tetrahedron(nodes_1, NAME, save_figure=True)
# Example 2: Positive signed volume (right-handed)
NAME = "Right-Handed Tetrahedron"
print(f"\nExample 2: {NAME}")
nodes_2 = np.array(
[
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
]
)
visualize_tetrahedron(nodes_2, NAME, save_figure=True)
# Example 3: Negative signed volume (left-handed / inverted)
NAME = "Left-Handed Tetrahedron"
print(f"\nExample 3: {NAME}")
nodes_3 = np.array(
[
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0], # Node 1
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0], # Node 2
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0], # Node 3
]
)
# Connectivity is [0, 2, 1, 3] - swapped nodes 1 and 2
nodes_3_inverted = nodes_3[[0, 2, 1, 3]]
visualize_tetrahedron(nodes_3_inverted, NAME, save_figure=True)
# Example 4: Degenerate tetrahedron (zero volume)
NAME = "Degenerate Tetrahedron"
print(f"\nExample 4: {NAME}")
nodes_4 = np.array(
[
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.3, 0.3, 0.0], # Co-planar with other nodes
]
)
visualize_tetrahedron(nodes_4, NAME, save_figure=True)
# Example 5: Random tetrahedron
NAME = "Random Tetrahedron"
print(f"\nExample 5: {NAME}")
nodes_5 = np.array(
[
[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
[1.8, 0.2, 1.1],
[0.1, 1.5, 0.3],
[1.3, 1.9, 2.0],
]
)
visualize_tetrahedron(nodes_5, NAME, save_figure=True)
# Example 6: Regular tetrahedron (for maximum skew test, has zero skew)
NAME = "Regular Tetrahedron"
print(f"\nExample 6: {NAME}")
nodes_6 = np.array(
[
[0.0, 0.0, 2.0],
[2.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 2.0, 0.0],
[2.0, 2.0, 2.0],
]
)
visualize_tetrahedron(nodes_6, NAME, save_figure=True)
plt.show()