Defeaturing
Defeaturing is accomplished by specifying a voxel threshold. A cluster of voxels, defined as two or more voxels that share a face (edge and node sharing do not constitute a cluster) with count at or above the threshold will be preserved, whereas a cluster of voxels with a count below the threshold will be eliminated through resorption into the surrounding material.
Example
With Python, we created a segmentation of four circular blobs with noise placed randomly in a bounding box, shown in left of the figure below. The segmentation file blobs.npy was then used as the input to automesh with the defeature command. The output file blobs_defeatured.npy is shown in the right of the figure. The threshold was set to 20 voxels.
automesh defeature -i blobs.npy -o blobs_defeatured.npy -m 20
Both the segmentation files, original and defeatured, were then converted to a mesh and visualized in Hexalab.
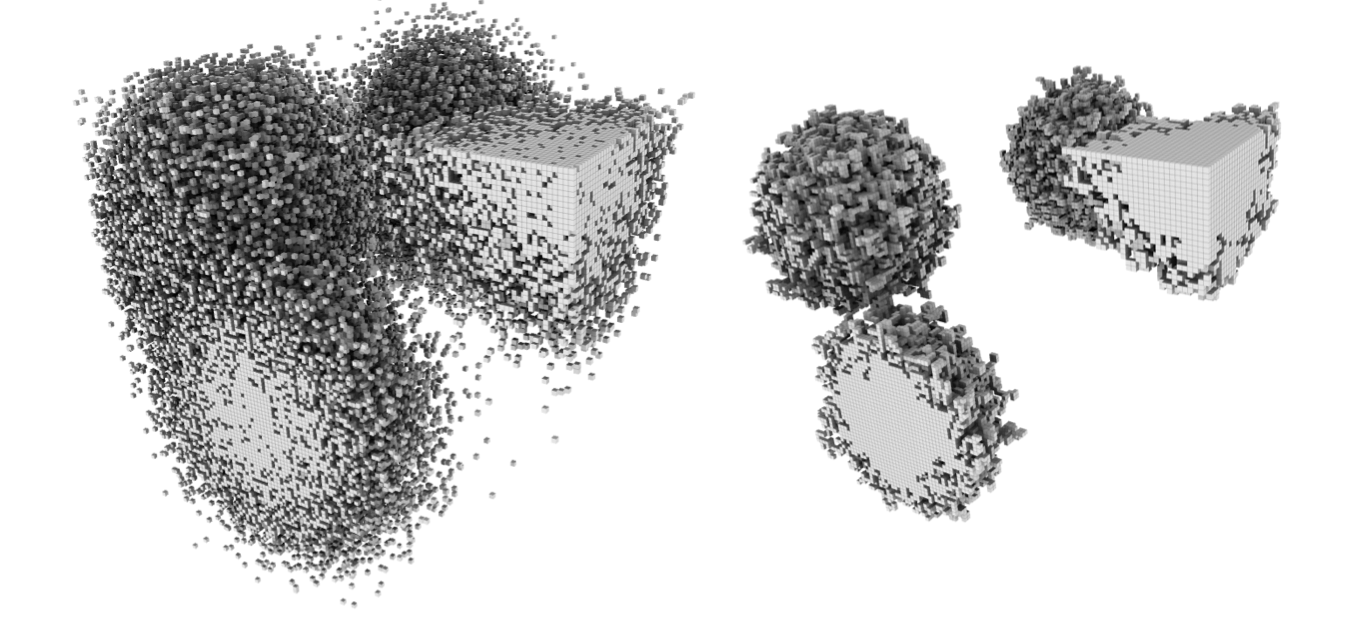
Figure: (left) Four circular blobs with noise (blobs.npy) used as input to the defeature command, (right) the output defeatured segmentation (blobs_defeatured.npy).
Source
defeature.py
r"""This module creates spheres and blobs inside of a domain for the purposes
of illustrating the defeature command.
Example:
source ~/autotwin/automesh/.venv/bin/activate
cd ~/autotwin/automesh/book/analysis/defeature
python defeature.py
"""
import logging
from pathlib import Path
import random
import subprocess
from typing import Final
import numpy as np
DOMAIN_SIZE: Final[int] = 128
NUM_SPHERES: Final[int] = 4
RADIUS_MAX: Final[int] = 20
FN_SPHERE_STEM = "spheres"
FN_BLOB_STEM = "blobs"
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format="%(levelname)s: %(message)s",
)
def create_spheres(data: np.ndarray, num_spheres: int, radius_max: int) -> None:
"""Creates random spheres in a 3D binary array.
Parameters:
data: A 3D binary array representing the domain.
num_spheres: The number of spheres to create.
radius_max: The radius of the spheres.
"""
shape = data.shape
(xmin, ymin, zmin) = (0, 0, 0)
(xmax, ymax, zmax) = (shape[0] - 1, shape[1] - 1, shape[2] - 1)
for _ in range(num_spheres):
# Randomly choose a center for the sphere
center = np.array(
[
random.randint(xmin, xmax),
random.randint(ymin, ymax),
random.randint(zmin, zmax),
]
)
# Randomly choose a center for the sphere
radius = random.randint(1, radius_max)
# Create a grid of indices
z, y, x = np.indices(shape)
# Calculate the distance from the center
distance = np.sqrt(
(x - center[0]) ** 2 + (y - center[1]) ** 2 + (z - center[2]) ** 2
)
# Set the voxels within the radius to 1
data[distance <= radius] = 1
def create_blob(data: np.ndarray, center: np.ndarray, radius_max: int) -> None:
"""Creates a sphere-like blob in a 3D binary array.
Parameters:
data: A 3D binary array representing the domain.
center: The center of the blob.
radius_max: The maximum radius of the blob.
"""
# Create a grid of indices
z, y, x = np.indices(data.shape)
# Calculate the distance from the center
distance = np.sqrt(
(x - center[0]) ** 2 + (y - center[1]) ** 2 + (z - center[2]) ** 2
)
# Create a random radius for each voxel based on a Gaussian distribution
radius_variation = np.random.normal(
loc=radius_max, scale=radius_max * 0.5, size=data.shape
)
# Set the voxels to 1 if they are within the radius variation
data[distance <= radius_variation] = 1
def create_blobs(data: np.ndarray, num_blobs: int, radius_max: int) -> None:
"""Create a number of sphere-like blobs in a 3D binary array.
Parameters:
data: A 3D binary array representing the domain.
num_blobs: The number of blobs to create.
radius_max: The maximum radius of the blobs.
"""
shape = data.shape
(xmin, ymin, zmin) = (0, 0, 0)
(xmax, ymax, zmax) = (shape[0] - 1, shape[1] - 1, shape[2] - 1)
for _ in range(num_blobs):
# Randomly choose a center for the blob
center = np.array(
[
random.randint(xmin, xmax),
random.randint(ymin, ymax),
random.randint(zmin, zmax),
]
)
# Create a blob at the center
create_blob(data=data, center=center, radius_max=radius_max)
def run_commands(commands: list) -> None:
"""Run a list of commands in the shell.
Parameters:
commands: A list of command strings to run.
"""
for command in commands:
try:
logging.info("Running command: %s", " ".join(command))
result = subprocess.run(command, check=True, capture_output=True, text=True)
logging.info("Command output: %s", result.stdout)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
logging.error("Error running command:")
logging.error("Command: %s", " ".join(command))
logging.error("Return code: %s", e.returncode)
logging.error("Standard Output: %s", e.stdout)
logging.error("Standard Error: %s", e.stderr)
def spheres():
"""Create and save a 3D binary array with random spheres."""
# Initialize the domain filled with zeros
domain = np.zeros((DOMAIN_SIZE, DOMAIN_SIZE, DOMAIN_SIZE), dtype=np.uint8)
# Create spheres in the domain
create_spheres(data=domain, num_spheres=NUM_SPHERES, radius_max=RADIUS_MAX)
# Save the data to a .npy file
FN_SPHERE = f"{FN_SPHERE_STEM}.npy"
np.save(FN_SPHERE, domain)
print(f"The domain with spheres has been saved to:\n{FN_SPHERE}.")
# Create the mesh with automesh
automesh = Path("~/autotwin/automesh/target/release/automesh").expanduser()
assert automesh.is_file(), f"automesh not found at {automesh}"
FN_SPHERE_EXO = f"{FN_SPHERE_STEM}.exo"
FN_SPHERE_MESH = f"{FN_SPHERE_STEM}.mesh"
commands = [
[
str(automesh),
"mesh",
"hex",
"-i",
str(FN_SPHERE),
"-o",
str(FN_SPHERE_EXO),
"-r",
"0",
],
[
str(automesh),
"mesh",
"hex",
"-i",
str(FN_SPHERE),
"-o",
str(FN_SPHERE_MESH),
"-r",
"0",
],
]
run_commands(commands=commands)
def blobs():
"""Create and save a 3D binary array with random blobs."""
# Initialize the domain filled with zeros
domain = np.zeros((DOMAIN_SIZE, DOMAIN_SIZE, DOMAIN_SIZE), dtype=np.uint8)
# Create blobs in the domain
create_blobs(data=domain, num_blobs=NUM_SPHERES, radius_max=RADIUS_MAX)
# Save the data to a .npy file
FN_BLOB = f"{FN_BLOB_STEM}.npy"
FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED = f"{FN_BLOB_STEM}_defeatured.npy"
np.save(FN_BLOB, domain)
print(f"The domain with blobs has been saved to:\n{FN_BLOB}.")
# Create the mesh with automesh
automesh = Path("~/autotwin/automesh/target/release/automesh").expanduser()
assert automesh.is_file(), f"automesh not found at {automesh}"
FN_BLOB_EXO = f"{FN_BLOB_STEM}.exo"
FN_BLOB_MESH = f"{FN_BLOB_STEM}.mesh"
FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED_EXO = f"{FN_BLOB_STEM}_defeatured.exo"
FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED_MESH = f"{FN_BLOB_STEM}_defeatured.mesh"
commands = [
[
str(automesh),
"mesh",
"hex",
"-i",
str(FN_BLOB),
"-o",
str(FN_BLOB_EXO),
"-r",
"0",
],
[
str(automesh),
"mesh",
"hex",
"-i",
str(FN_BLOB),
"-o",
str(FN_BLOB_MESH),
"-r",
"0",
],
[
str(automesh),
"defeature",
"-i",
str(FN_BLOB),
"-o",
str(FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED),
"-m",
"20",
],
[
str(automesh),
"mesh",
"hex",
"-i",
str(FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED),
"-o",
str(FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED_EXO),
"-r",
"0",
],
[
str(automesh),
"mesh",
"hex",
"-i",
str(FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED),
"-o",
str(FN_BLOB_DEFEATURED_MESH),
"-r",
"0",
],
]
run_commands(commands=commands)
if __name__ == "__main__":
spheres()
blobs()