Dualization
Dualization is the process of using a primal mesh to construct a dual mesh. Dualization can be performed on 2D/3D surface meshes composed of quadrilateral elements, and 3D volumetric meshes composed of hexahedral elements. Both quadrilateral and hexahedral elements will be discussed.
Quadtree
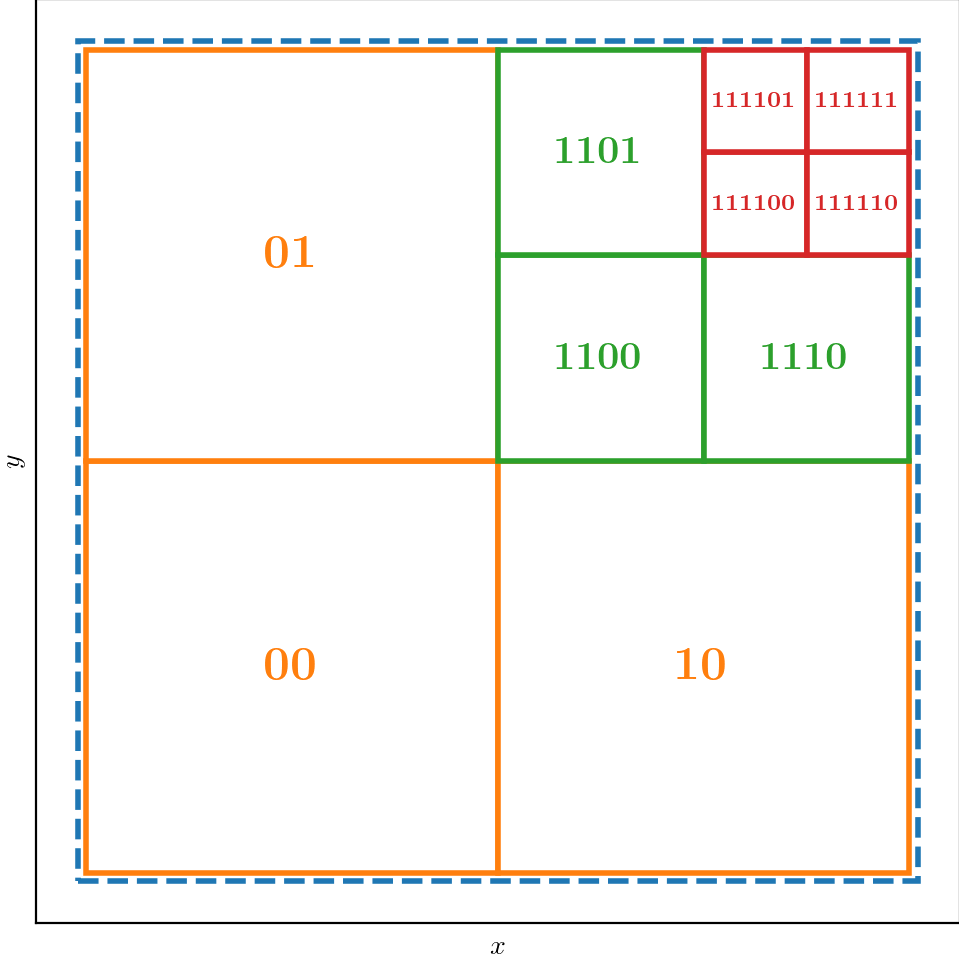
With plot_quadtree_convention.py, we create the following index scheme:
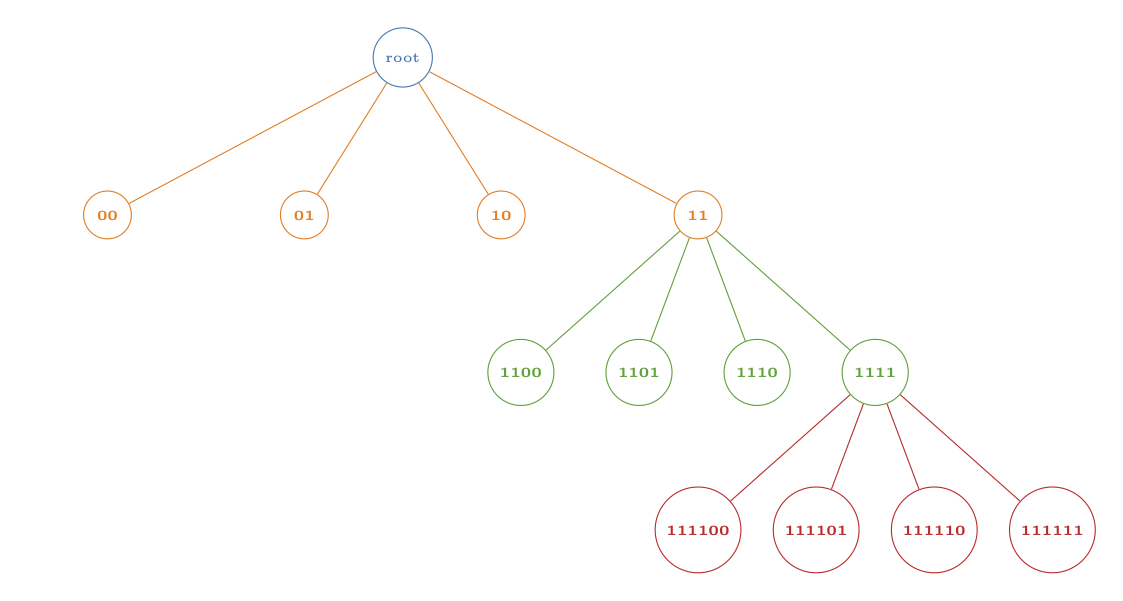
With fig_quadtree.tex, we create the following image of the inverted tree:
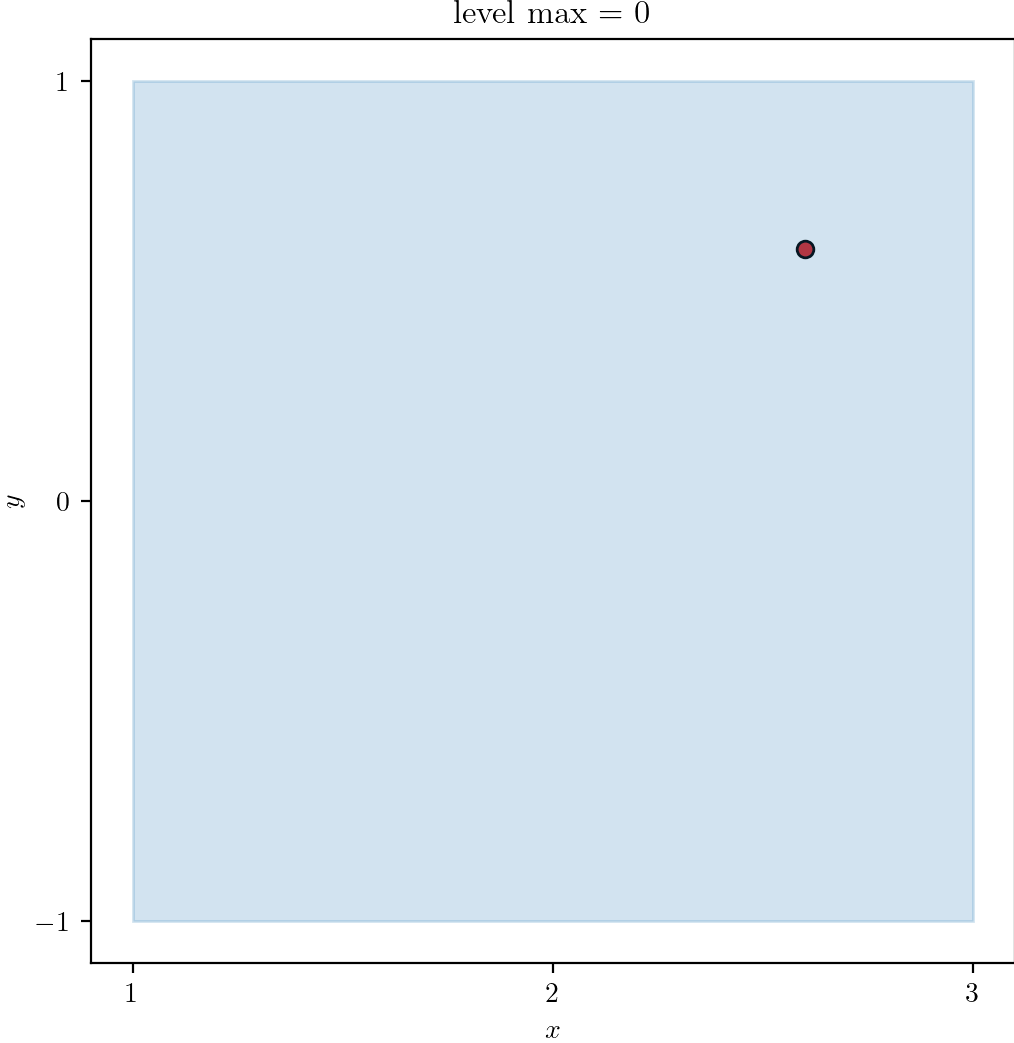
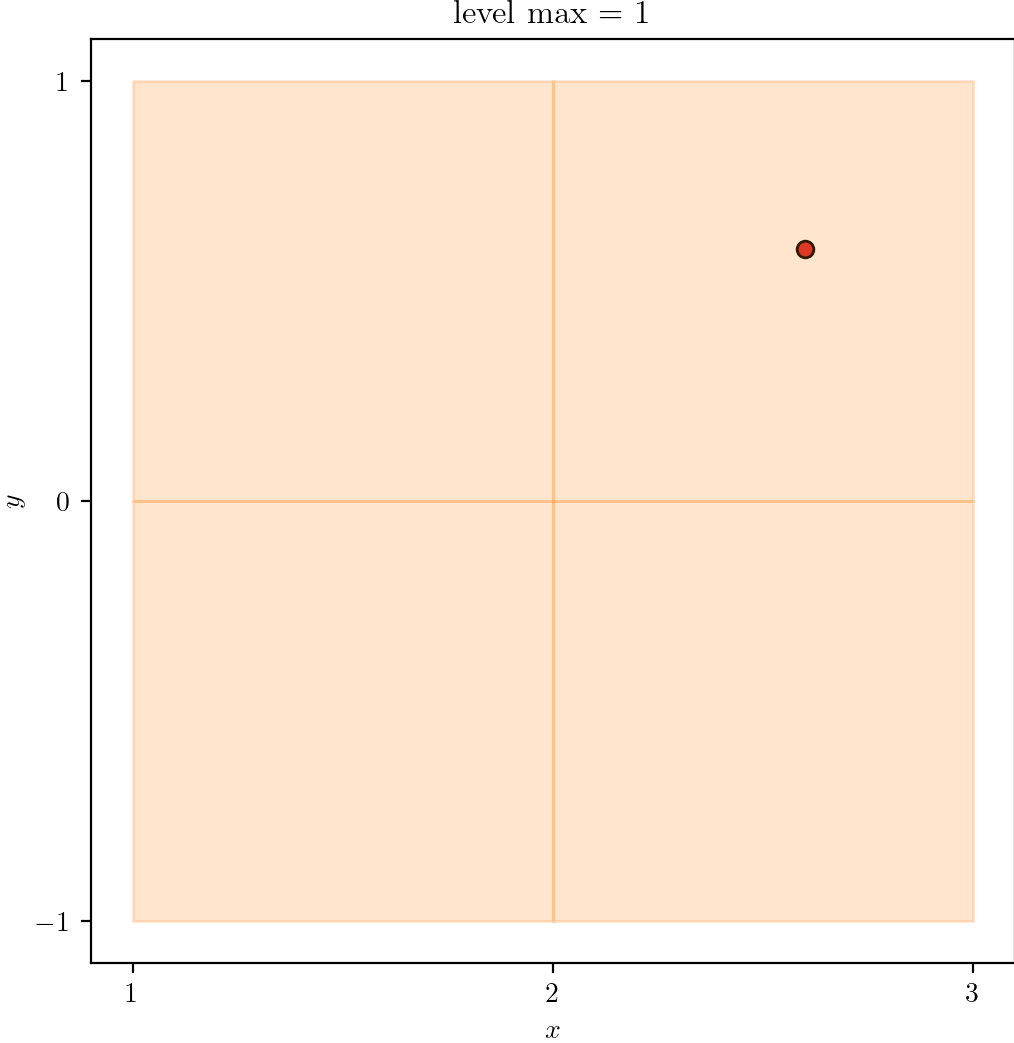
With plot_quadtree.py, we plot a domain
- A square domain
L0 - Single point at
(2.6, 0.6)to trigger refinement.
| Level 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
 |  | 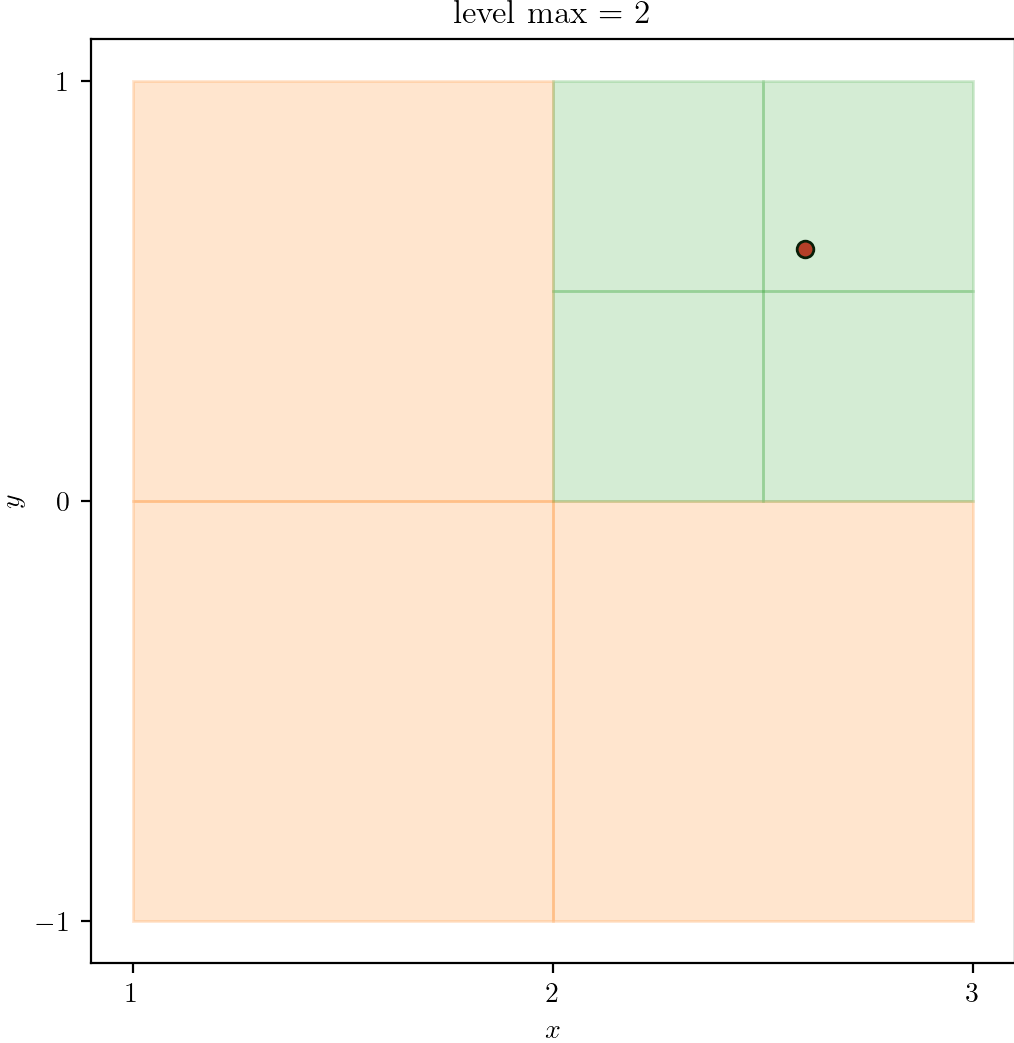 |
| 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|
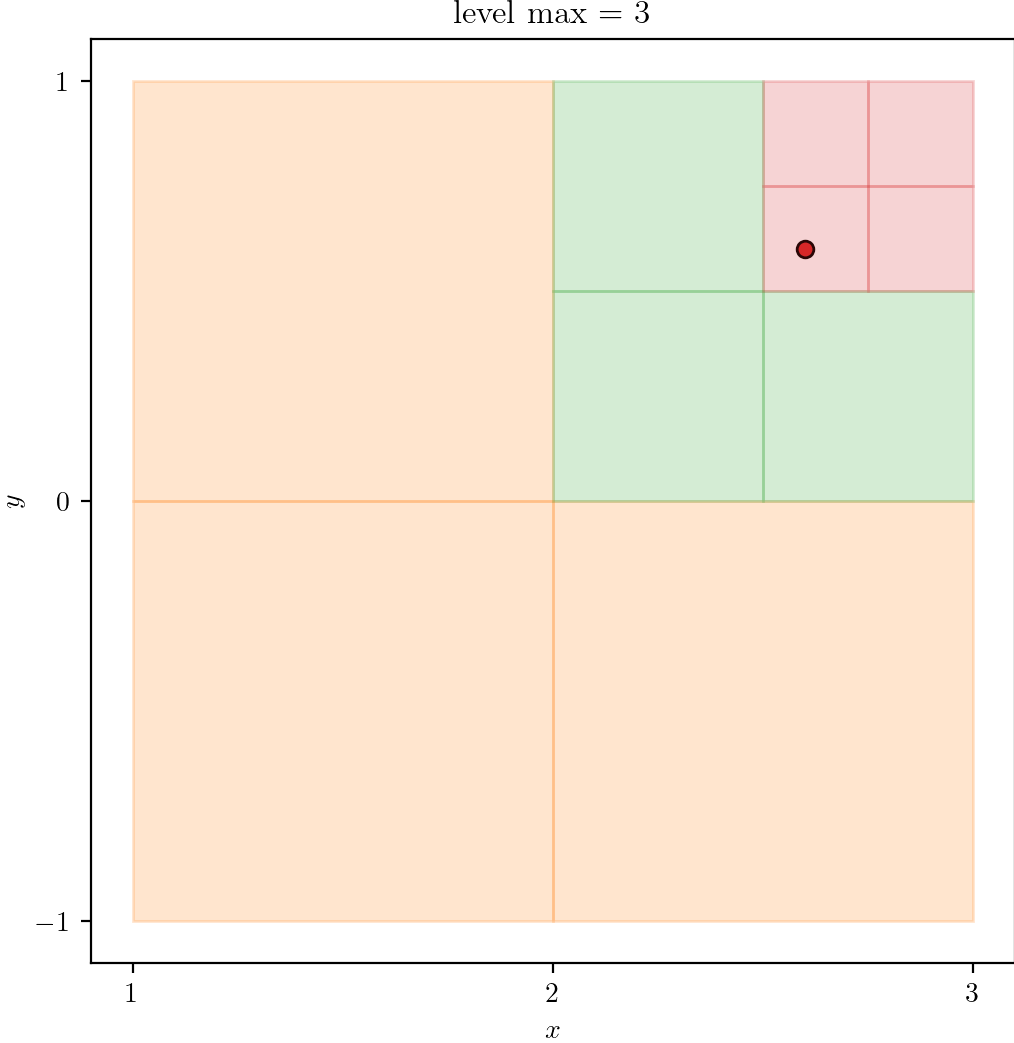 | 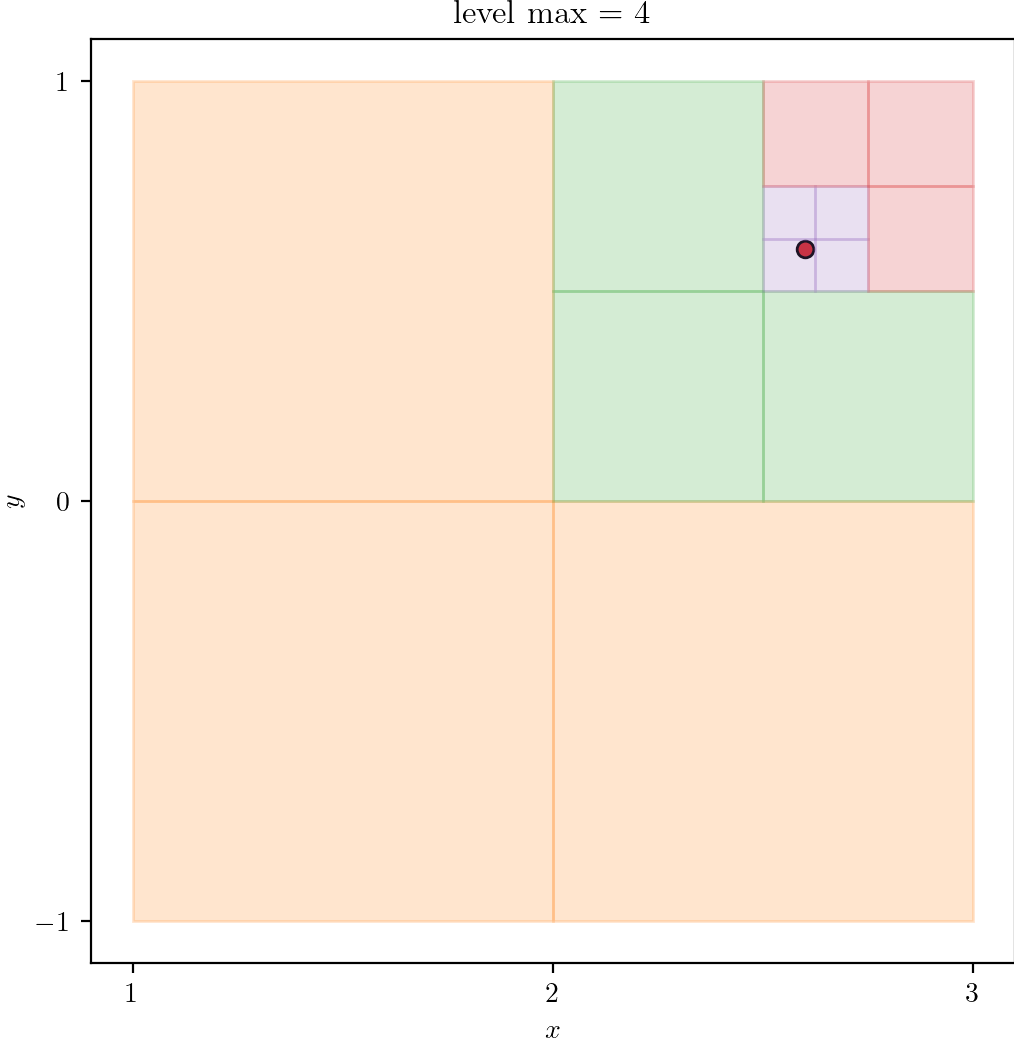 | 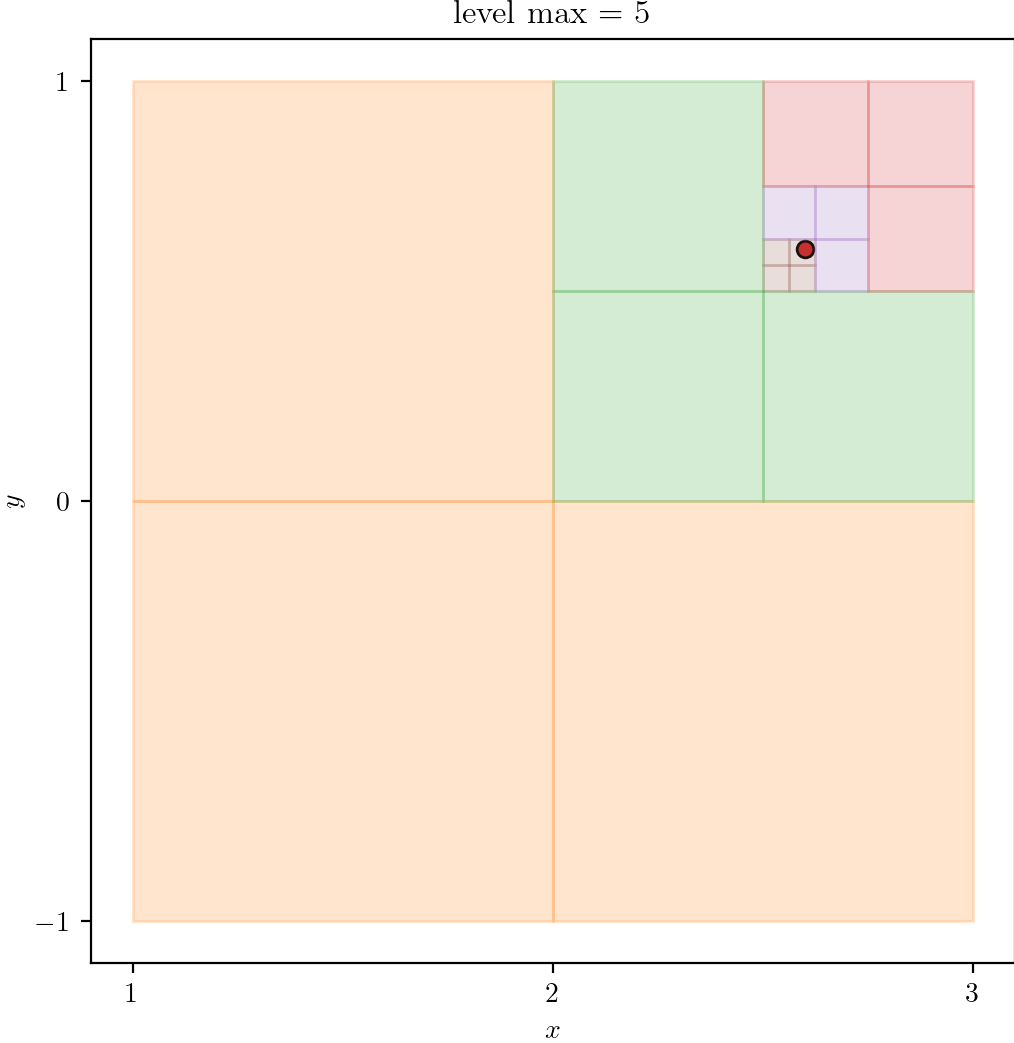 |
Circle from Segmentation
We illustrate the segmentation start point as it applies to quadtree formation.
- For a segmentation at a given resolution of pixels, we immerse the segmentation into a single-cell (
L0) quadtree domain. - We pad the segmentation margins with void (segmentation ID
0) such that the pixel count in all directions ( and )- is the same, and
- is divisible by 2 for cell subdivisions.
- For each cell in the quadtree, we process the cells recursively and ask this question: Does the cell contain more than one material? If yes, then subdivide; if no, then do not subdivide.
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|
Circle from Boundary
We illustrate the boundary start point as it applies to quadtree formation.
- We define a boundary as directed series of connected, discrete points that create a closed-loop, non-intersecting path.
- We immerse the boundary into a single-cell (
L0) quadtree domain. - For each cell in the quadtree, we process the cells recursively and ask this question: Does the cell contain at least one boundary point? If yes, then subdivide; if no, then do not subdivide.
Consider a boundary of a circle defined by discrete (x, y) points.
| Level 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|
Circle from Tesellation
We illustrate the tesellation as it applies to quadtree formation.
- We immerse the tesellation into a single-cell (
L0) quadtree domain. - We create a boundary of the tesellation with points that lie on the boundary of the tesellation.
- We immerse the boundary into a single-cell (
L0) quadtree domain. - For each cell in the quadtree, we process the cells recursively and ask this question: Does the cell contain at least one boundary point? If yes, then subdivide; if no, then do not subdivide.
Quarter Plate
With Python, we produce a Quadtree with zero to five levels of refinement. Refinement is triggered based on whether or not a cell contains one or more seed points, shown as points along the quarter circle centered at (4, 0).
| Level 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|
Octree
Sphere
Consider a boundary of a sphere defined by a discrete triangular tesselation.
References
- https://github.com/sandialabs/sibl/blob/master/geo/doc/quadtree.md
- https://github.com/sandialabs/sibl/blob/master/geo/doc/dual_quad_transitions.md
- https://github.com/sandialabs/sibl/blob/master/geo/doc/dual/lesson_11.md
Source
quadtree_plot.py